LCEL 全名 LangChain Expression Language, 是一種描述 LangChain 架構的語言。最大的特徵就是看到 A = B | C | D 這種表示法 – 說明了 LCEL 串接多個可執行單元的特性,是 LangChain 的進階實現。而 ‘|’ 的理解和 Linux 的 pipe 很像,它是非同步的串接。
舉例來說,一個 LLM 的 LangChain 可以表示為:
chain = prompt | LLM model | Output Parser
依序做好這三件事:有方向性的提示、強大的大語言模型、友善的輸出格式,就可以提升使用者體驗。
但是顯然這樣還不太夠,比方說,LLM 需要查一筆它沒被訓練過的資料,在上面的 pipe 就無法做到。換個例子,我想幫 AI 助理取個名字,它也會說好。但是一轉眼什麼山盟海誓都忘光了!

顯然,我們要有個負責的 agent,把 function call 的能力加進來;而且 call 完之後,還要餵給 LLM 做 “人性化" 的自然語言潤飾。這是一個循環的路徑,直到 AI 判斷它不再需要任何外部工具,就可以結束迴圈,跟使用者報告最終結果了。
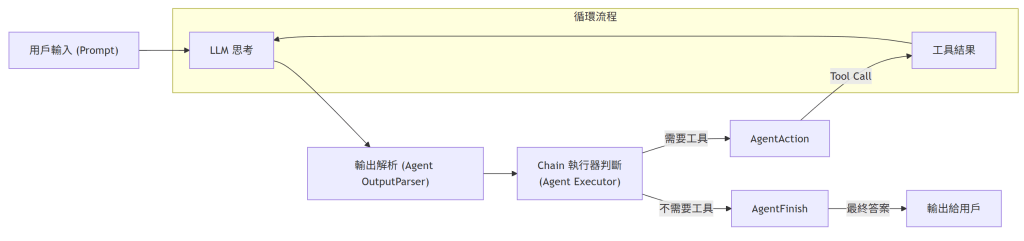
那麼這個 code 長什麼樣子? 首先把基本元件準備好:
# 初始化模型
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o", temperature=0)
# 將工具打包成列表
tools = [get_current_weather] # 以問天氣的函式為例
# 給出配合 function 的 prompt
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", "你是天氣助理,請根據工具的結果來回答問題。"),
("placeholder", "{chat_history}"), # 預留給歷史訊息
("human", "{input}"), # 真正的輸入
("placeholder", "{agent_scratchpad}"), # 於思考和記錄中間步驟
]
)創建 agent
# 創建 Tool Calling Agent
# 將 LLM、Prompt 和 Tools 組合起來,處理 Function Calling 的所有複雜流程
agent = create_tool_calling_agent(llm, tools, prompt)執行 agent
# 創建執行器, 跑 模型思考 -> 呼叫工具 -> 再次思考 -> 輸出答案的循環
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=tools, verbose=True)設計人機介面
def run_langchain_example(user_prompt: str):
print(f"👤 用戶提問: {user_prompt}")
# 使用 invoke 運行 Agent,LangChain 會自動管理多輪 API 呼叫
result = agent_executor.invoke({"input": user_prompt})
print(f"🌟 最終答案: {result['output']}")測試案例
# 示範一:Agent 判斷需要呼叫工具
run_langchain_example("請問新竹現在的天氣怎麼樣?請告訴我攝氏溫度。")
# 示範二:Agent 判斷不需要呼叫工具,直接回答
run_langchain_example("什麼是 LLM?請用中文簡短回答。")這邊要留意的是,第一個問天氣的問題,LLM 顯然要用到 tool 去外面問,第二個問題不需要即時的資料,所以它自己回答就好。
意猶未盡的讀者可能好奇 function 長怎樣? 其實就很一般,主要的特色是用 @tool decorator。這樣可以獲得很多好處,最重要的一點是 agent 都認得它的 JSON 輸出,方便資料異步流動。
# LangChain 會自動將這個 Python 函數轉換成模型可理解的 JSON Schema
from langchain_core.tools import tool
@tool
def get_current_weather(location: str, unit: str = "celsius") -> str:
if "新竹" in location or "hsinchu" in location.lower():
return "風大啦! 新竹就是風大啦!"
else:
return f"我不知道 {location} 的天氣啦!"另外,追根究柢的讀者可能想問,code 裡面怎麼沒看到 ‘|’? 它跑那裡去了? 沒錯,上面講的都是 agent,它比較進階,可以動態跑流程。反而 LCEL 只是 LangChain 的實行方式,它就是一個線性的 chain。
我們由奢返儉,回過頭來看 LCEL,它不能跟 agent 比,只能打敗傳統的 LangChain。標為紅色的是 LCEL 特色的 coding style。
def demonstrate_legacy_chain():
# 定義模型
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
# 定義 Prompt Template
template = "Translate English text to Chinese: {text}"
prompt = PromptTemplate(template=template, input_variables=["text"])
# 建立 Chain (透過類別組合)
# 缺點:語法較冗長,看不到資料流向,且 output 通常包含原始 meta data
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
# 執行
input_text = "Make American Great Again!"
result = chain.run(input_text)VS
def demonstrate_lcel():
# 定義模型
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
# 定義 Prompt Template, 使用更現代的 ChatPromptTemplate
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("Translate English text to Chinese: {text}")
# 定義 Output Parser (將 AI Message 轉為純字串)
output_parser = StrOutputParser()
# 建立 Chain (使用 Pipe '|' 運算符)
# 優點:Unix 風格管道,由左至右邏輯清晰,易於修改和擴展
chain = prompt | model | output_parser
# 執行
input_text = "Make American Great Again!"
result = chain.invoke({"text": input_text})這兩個都是一次性的 Q&A。