繼上次的 key format 之後, 又多了一個進階題叫做 order format. 根據 [1] 的 p. 20, 有 3 種 order formats. 價格也略有不同, 當然大客戶比較便宜 (large adopter) 是無庸置疑的. 為何 fomrat 3 比較貴呢?
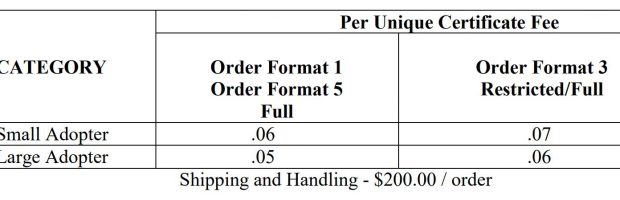
根據定義, order format 1/3/5 的差異可以用 certificate (證書) / key 和 full / restricted 的排列組合來表現. 如下表, order foramt 3 的範圍最廣, license fee 也就最貴, Order format 1 居中, Order foramt 5 的範圍最小.
| Certificate\Key |
Full |
Restricted |
| Full |
Order Format 1/3/5 |
Order Format 1/3 |
| Restricted |
Order Format 3 |
Order Format 3 |
根據 [1] 的 P.2, 證書和 key 的說明如下:
1.11 “Device Certificate” means a cryptographically encoded value which may be provided by
DTLA or its designee which authorizes a device to exchange certain Commercial Entertainment
Content.
1.12 “Device Keys” means cryptographic values which may be provided by DTLA or its designee
for use in devices, and include the “Private Device Key” and the “Public Device Key” and keys
associated with Restricted Authentication, all identified in the Specification.
DTCP 的 content 裡面包括一個 CCI (copy control information), CCI 裡面存放 EMI (encryption mode indicator) 來標記可以做甚麼樣的加密: copy free, copy never, copy once.
當 copy once 的 content 被 DTCP sink 處理的時候, 它的 EMI 若改記為 copy no more, 後續就可以只做 restricted authentication ([3] 的 P.891). 假如 content 被標記為 “copy never", 就必須做 full authentication.

當需要做 full authentication 時, source 和 sink 要互相檢查對方的證書 (certificate), 然後做 key exchange. Restricted authentication 時, sink 只要向 source 證明他們的 secret key 都一樣.

因此對於一個 recorder 來說, 它可能可以支援 full authentication certificate (計算能力夠強), 也可能只支援 restricted authetication certificate (計算能力弱). 為了降低計算需求, 採用 restricted authetication 比較方便. 但 key 為何又分為 full 和 restricted 呢? 這牽涉到 full authentication 下要選擇 order format 1 或是 5?
我們可以發現 restricted certificate 就不能選 full key, 但是 full certificate 可以選 restricted key. 我推測這是給予 full certificate 去選擇要把 copy once 減一成為 copy never (full key) 或是單純降為 copy no more (restricted key) 的權利.
客戶又問了 AP 和 AL 是 0 還是 1?
AL flag (1 bit). Additional Localization flag. The AL flag is set to value of one to indicate that the associated device is capable of performing the additional localization test, otherwise shall be set to value of zero.
AP flag (1 bit). Authentication Proxy flag. A device certificate with an AP flag value of one is used by a DTCP bus bridge device, which receives a content stream using a sink function and retransmits that stream to another bus using a source function5.
首先看 Localization flag 是什麼? 根據 [4], 它在 DTCP + 1394 的規格也出現過. IEEE 1394 就是那個已經沒人在用的 DV 規格, 但 localization 的精神應該是一樣的. 基本上, 它要避免利用網路來遠端破解 DTCP, 所以要用網路封包的 round trip time 來檢查 sink 是否在很遠的地方. 如果我們要遠端 debug DTCP-IP 的 content, 我當然希望是 AL = 0. 但正常的產品給 AL = 1 即可.
什麼是 authentication proxy 呢? 顧名思義, 這是不是一個 DTCP 橋接器, 把左手的 DTCP 送給右手. 做為一個 recorder 來說, AP 應該要為 0. 因為不能把收進來的 DTCP-IP 不解就直接寫進 time shift buffer 等下次用. 既然 DTCP-IP 和 Time shift buffer 的 key 不能共用, AP = 0 就好.
[Note]
- http://www.dtcp.com/documents/licensing/dtla-adopter-agreement.pdf
- ITU-T_J.95Y1999.PDF
- Multimedia Encryption and Authentication Techniques and Applications
- https://www.dtcp.com/documents/dtcp/info-20070615-dtcp-v1sf-rev-1-p-0.pdf